Understanding Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Deep Dive Into The Heart Of Economic Policy
So, let's get real here—federal reserve interest rates are the unsung heroes of the global economy, quietly pulling the strings behind the scenes. They're not just numbers on a screen or graphs in a report; they're the heartbeat of financial stability. If you're scratching your head right now, wondering what this all means, don't sweat it. We're about to break it down for you in a way that even your grandma could understand. Whether you're an investor, a student, or just someone trying to make sense of the financial world, this topic is crucial. It's like the secret sauce that makes the economy tick.
Think about it this way: when you hear about the stock market going up or down, inflation rising, or mortgage rates changing, the Federal Reserve is probably involved somewhere along the line. Their decisions on interest rates can impact everything from your credit card bill to the price of that new car you've been eyeing. It's a big deal, and understanding it can give you a leg up in navigating the financial landscape.
But why should you care? Well, because federal reserve interest rates can affect your wallet directly. Ever wondered why your savings account earns so little interest, or why your loan payments suddenly went up? The Fed has its hands in all of that. So, buckle up because we're about to take a deep dive into the world of federal reserve interest rates, and by the end of this, you'll be armed with knowledge that could save—or even make—you money.
Table of Contents
- What Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
- How Does the Federal Reserve Control Interest Rates?
- Why Do Interest Rates Matter?
- Effects on the Economy
- A Historical Perspective
- The Current Situation
- Impact on Personal Finance
- Tools Used by the Fed
- Future Directions
- Conclusion
What Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. Federal Reserve interest rates refer to the rate at which banks lend money to each other overnight. This might sound boring, but trust me, it's a big deal. The Fed sets a target range for this rate, known as the federal funds rate, which influences borrowing costs throughout the economy. It's like the domino effect—change the rate here, and you'll see ripples everywhere.
Now, you might be asking, why does this matter? Well, when the federal funds rate changes, it affects everything from mortgage rates to car loans to credit card interest rates. It’s kinda like the Fed is the DJ at a party, and the interest rate is the music. Change the tune, and the vibe of the whole party shifts. So yeah, it’s kinda a big deal.
Breaking It Down
Let’s break it down even further. The federal funds rate is essentially the cost of borrowing money for banks. When the Fed lowers this rate, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow money, which they then pass on to consumers in the form of lower interest rates on loans and credit cards. Conversely, when the Fed raises the rate, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can slow down spending and investment.
How Does the Federal Reserve Control Interest Rates?
The Fed has a few tricks up its sleeve when it comes to controlling interest rates. The main one is something called open market operations. This is where the Fed buys or sells government securities to influence the supply of money in the economy. It's like playing with a giant seesaw—buy more securities, and the seesaw tips one way; sell them, and it tips the other way.
Another tool the Fed uses is something called the discount rate. This is the interest rate the Fed charges banks for direct loans. By adjusting this rate, the Fed can influence how much banks are willing to lend to each other and, ultimately, to consumers.
Quantitative Easing and Tightening
Now, here’s where things get a little fancy. The Fed also uses something called quantitative easing (QE) and tightening to influence interest rates. QE is when the Fed buys large quantities of government bonds and other financial assets to inject money into the economy. It's like giving the economy a big boost when it's feeling sluggish. On the flip side, quantitative tightening is when the Fed reduces its bond holdings, which can slow down economic activity.
Why Do Interest Rates Matter?
Interest rates matter because they affect pretty much everything in the economy. They influence consumer spending, business investment, and even government policy. When rates are low, it’s cheaper to borrow money, which encourages spending and investment. This can lead to economic growth, job creation, and all that good stuff. But when rates are too high, it can slow down the economy, leading to job losses and economic downturns.
Think of it like driving a car. If the gas pedal is the economy, interest rates are the brakes and the accelerator. The Fed is the driver, deciding when to press the gas and when to hit the brakes. It’s a delicate balance, and getting it wrong can have serious consequences.
Key Takeaways
- Interest rates affect borrowing costs for consumers and businesses.
- Low rates can stimulate economic growth, while high rates can slow it down.
- The Fed uses various tools to influence rates and maintain economic stability.
Effects on the Economy
The effects of federal reserve interest rates on the economy are far-reaching. When rates are low, businesses are more likely to invest in new projects, hire more workers, and expand their operations. Consumers are also more likely to spend money on big-ticket items like houses and cars. It's like a snowball effect—more spending leads to more jobs, which leads to more spending, and so on.
But when rates are high, the opposite happens. Businesses tighten their belts, consumers cut back on spending, and the economy can slow down. It's a bit like putting the brakes on a speeding car—you need to slow down to avoid crashing, but if you brake too hard, you might skid off the road.
Real-World Examples
Take the 2008 financial crisis, for example. The Fed lowered interest rates to near-zero levels to stimulate the economy and prevent a deeper recession. It worked, but it also led to some unintended consequences, like asset bubbles in housing and stocks. On the flip side, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the Fed raised rates sharply to combat high inflation, which led to a deep recession but ultimately stabilized the economy.
A Historical Perspective
Looking back at history, the Fed’s role in controlling interest rates has evolved over time. In the early days, the Fed was more focused on maintaining the gold standard and controlling inflation. But as the economy grew more complex, the Fed’s role expanded to include promoting maximum employment and stabilizing prices.
Some of the most significant moments in Fed history include the Great Depression, where the Fed was criticized for not doing enough to prevent the crisis, and the Volcker era in the 1980s, where the Fed took bold action to combat inflation. These historical lessons continue to shape the Fed’s approach to interest rate policy today.
Lessons Learned
- The Great Depression taught the Fed the importance of acting quickly in a crisis.
- The Volcker era showed that tough measures, even if unpopular, can be necessary to stabilize the economy.
- The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the need for better regulation and oversight of financial markets.
The Current Situation
As of right now, the Fed is facing some unique challenges. With inflation running high and the economy recovering from the pandemic, the Fed has had to carefully balance raising rates to control inflation without stifling economic growth. It's like walking a tightrope—too much in one direction, and you could fall off.
Recent data shows that the Fed has been gradually raising interest rates, but the pace and extent of these increases remain uncertain. It's a bit like trying to predict the weather—there are a lot of variables at play, and things can change quickly.
What to Watch For
- Future Fed announcements on interest rate changes.
- Economic indicators like inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth.
- Global events that could impact the U.S. economy.
Impact on Personal Finance
So, how does all this affect you personally? Well, if you have a mortgage, car loan, or credit card, you're probably already feeling the effects of changing interest rates. Higher rates mean higher monthly payments, which can strain your budget. On the flip side, if you have savings, higher rates can mean better returns on your money.
It’s like playing a game of financial chess—you need to anticipate the Fed’s moves and adjust your strategy accordingly. Maybe it’s time to refinance that mortgage or lock in a fixed rate on your car loan before rates go up even more.
Tips for Managing Your Finances
- Pay down high-interest debt as quickly as possible.
- Consider locking in fixed rates on loans if rates are expected to rise.
- Keep an eye on savings account rates for better returns.
Tools Used by the Fed
As we’ve already touched on, the Fed has a few key tools in its toolkit when it comes to controlling interest rates. Open market operations, the discount rate, and quantitative easing/tightening are just a few of the methods the Fed uses to influence the economy. But these tools aren’t one-size-fits-all. The Fed has to carefully consider the current economic situation and adjust its approach accordingly.
It’s like a chef with a recipe book. Sometimes you need to add more spice, and sometimes you need to tone it down. The Fed has to get the recipe just right to keep the economy running smoothly.
Other Tools in the Toolbox
- Forward guidance—communicating future policy moves to influence market expectations.
- Reserve requirements—setting minimum amounts of reserves banks must hold.
- Capital requirements—ensuring banks have enough capital to withstand economic shocks.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the Fed faces some big challenges. Climate change, technological disruption, and global economic shifts are just a few of the factors that could impact interest rate policy in the coming years. The Fed will need to be agile and adaptable to navigate these challenges successfully.
But one thing is certain—the Fed will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the economy. Whether it’s through interest rate adjustments, regulatory changes, or new policy initiatives, the Fed will remain at the center of the financial world.
What’s Next?
- Monitoring global economic trends and their impact on the U.S. economy.
- Adapting to new challenges like climate change and technological disruption.
- Continuing to refine policy tools to better serve the needs of the economy.
Conclusion
So, there you have it—a deep dive into federal reserve interest rates and why they matter. From influencing the economy to affecting your personal finances, the Fed’s decisions on interest rates have far-reaching consequences. Understanding these dynamics can empower you to make better financial decisions and navigate the complex world of economics with confidence.
As we wrap up, remember that the Fed’s role is to maintain economic stability and promote growth. It’s not an easy job, and mistakes can happen, but the Fed is constantly learning and adapting to new challenges. So, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just someone trying to make sense of the financial world, keep an eye on the Fed and its policies—they could make a big difference in your life.
And hey, if you’ve made it this far, give yourself a pat on the back. You’ve just gained some serious knowledge about one of the most important aspects of the economy. Now go out there and put it to good use. And don’t forget to share this article with your friends—they’ll thank you for it!
NBC: The Network That Defined American Television
Spring Has Sprung: Celebrating The First Day Of Spring
Nowruz: The Celebration That Brings Spring And Renewal To Life
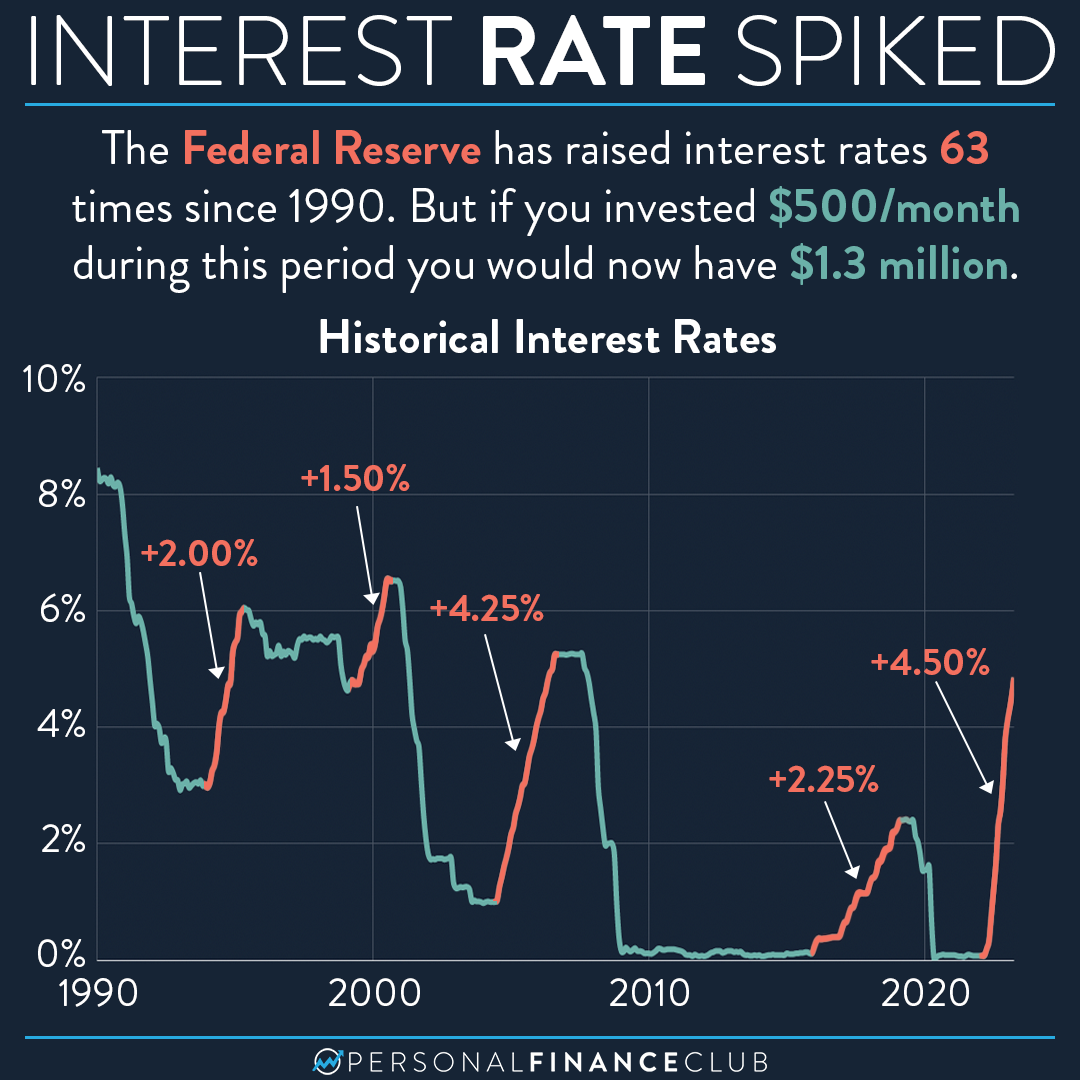
Federal Reserve Raising Interest Rates Personal Finance Club

Federal Reserve raises interest rates by 50 basis points

Federal Reserve interest rates FloreGawaine