When Does The Year 1404 Begin And What You Need To Know
Let's talk about something that might intrigue you—when exactly does the year 1404 begin? If you're into Persian calendars or just curious about how different cultures mark time, this is the perfect place for you. We’re diving deep into the details of the Persian calendar, exploring its unique structure, and answering all the questions buzzing in your mind. So, buckle up because we’re about to take a trip through history, culture, and some fascinating facts.
This article isn’t just about numbers or dates; it’s about understanding the significance of the Persian calendar in modern times. Imagine a world where timekeeping isn’t just about ticking clocks but also about honoring traditions passed down through generations. That’s what the Persian calendar represents—a blend of ancient wisdom and contemporary relevance.
By the end of this article, you'll not only know when the year 1404 begins but also appreciate the depth and intricacies of the Persian calendar system. So, whether you're planning a trip to Iran or simply curious about cultural nuances, stick around because this journey is going to be eye-opening.
Here’s a quick glance at what we’ll cover:
- The History and Origins of the Persian Calendar
- Understanding the Structure of the Persian Calendar
- When Does the Year 1404 Begin?
- Cultural Celebrations Around the Persian New Year
- Comparing the Persian Calendar with Other Calendars
- The Significance of the Persian Calendar in Modern Times
The History and Origins of the Persian Calendar
Let’s rewind a bit and dive into the origins of the Persian calendar. Imagine ancient Persia, a land rich in culture and knowledge. The Persian calendar, also known as the Solar Hijri calendar, has its roots dating back thousands of years. It's not just a system of counting days; it’s a reflection of the celestial movements observed by early astronomers.
Historians believe that the foundations of the Persian calendar were laid during the Achaemenid Empire. The calendar was further refined during the Sassanian period, making it one of the most accurate solar calendars in existence. The calendar is based on the Earth's orbit around the Sun, which makes it incredibly precise in terms of seasons and equinoxes.
Fast forward to modern times, the Persian calendar remains a vital part of Iranian culture. It’s used alongside the Gregorian calendar, especially for cultural and religious events. So, if you’re ever in Iran, don’t be surprised to see two dates on calendars—one in the Gregorian system and the other in the Persian system.
Key Milestones in the Development of the Persian Calendar
- Achaemenid Era: Early foundations laid down.
- Sassanian Era: Refined and standardized.
- Modern Era: Continued use and adaptation.
Understanding the Structure of the Persian Calendar
Alright, let’s break down the structure of the Persian calendar. Unlike the Gregorian calendar, which divides the year into twelve months of varying lengths, the Persian calendar follows a more consistent pattern. Each year consists of twelve months, but the first six months have 31 days each, the next five have 30 days, and the final month has 29 days in a common year or 30 days in a leap year.
This structure ensures that the calendar aligns closely with the solar year, making it highly accurate in tracking seasonal changes. The year begins with the vernal equinox, which usually falls around March 21st in the Gregorian calendar. This alignment with the natural cycle of the Earth’s orbit is what makes the Persian calendar so special.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Months 1-6: 31 days each.
- Months 7-11: 30 days each.
- Month 12: 29 or 30 days depending on leap year.
How Does Leap Year Work in the Persian Calendar?
Leap years in the Persian calendar occur once every four years, similar to the Gregorian system. However, the calculation is slightly different. Instead of adding a day to February, the Persian calendar adds an extra day to the last month of the year, Esfand. This ensures that the calendar remains in sync with the solar year.
When Does the Year 1404 Begin?
Now, let’s get to the heart of the matter. When does the year 1404 begin? According to the Persian calendar, the year 1404 will start with the vernal equinox in 2025. This usually falls on March 20th or 21st, depending on the exact astronomical alignment. So, if you're marking your calendars, make sure to note down this date.
Interestingly, the Persian New Year, known as Nowruz, is celebrated with great fanfare. It’s a time for families to gather, enjoy traditional foods, and participate in cultural rituals. The celebration lasts for thirteen days, culminating in the outdoor picnic known as Sizdah Bedar.
Why Is the Vernal Equinox So Important?
The vernal equinox marks the beginning of spring and the start of the new year in the Persian calendar. It’s a time of renewal and rebirth, symbolizing the cycle of life. The equinox occurs when the Sun crosses the celestial equator, making day and night almost equal in length. This natural phenomenon is what the Persian calendar is based on, making it deeply connected to the Earth’s rhythms.
Cultural Celebrations Around the Persian New Year
Nowruz, the Persian New Year, is not just a date on the calendar; it’s a vibrant celebration that brings communities together. Imagine streets adorned with colorful decorations, families preparing traditional dishes like Sabzi Polo Mahi, and children receiving new clothes as gifts. It’s a time of joy, unity, and gratitude.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Nowruz is the Haft Sin table. Families set up a table with seven items that start with the letter "S" in Persian. These items symbolize different aspects of life, such as health, wealth, and prosperity. The Haft Sin table is a beautiful representation of Persian culture and tradition.
Here’s a list of the seven items commonly found on a Haft Sin table:
- Sabzeh: Sprouts symbolizing rebirth.
- Samanu: Sweet pudding symbolizing affluence.
- Senjed: Dried fruit symbolizing love.
- Serkeh: Vinegar symbolizing patience.
- Seeb: Apples symbolizing beauty and health.
- Somagh: Sumac symbolizing the color of sunrise.
- Sekkeh: Coins symbolizing wealth.
How Is Nowruz Celebrated Outside Iran?
Nowruz is celebrated not only in Iran but also in many other countries with Persian influences, such as Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Azerbaijan. Each region adds its own unique twist to the celebrations, making it a diverse and inclusive festival. For example, in Afghanistan, people often fly kites during Nowruz, while in Azerbaijan, traditional dances and music are an integral part of the festivities.
Comparing the Persian Calendar with Other Calendars
Let’s compare the Persian calendar with other widely used calendars, such as the Gregorian and Islamic calendars. Each calendar has its own unique features and purposes, but they all serve the same fundamental function—tracking time.
The Gregorian calendar, used globally for most official purposes, is a solar calendar with 365 days in a common year and 366 days in a leap year. The Islamic calendar, on the other hand, is a lunar calendar with 354 or 355 days in a year. This difference in structure means that Islamic months do not align with the seasons, unlike the Persian and Gregorian calendars.
Here’s a quick comparison:
- Persian Calendar: Solar, based on vernal equinox.
- Gregorian Calendar: Solar, used globally.
- Islamic Calendar: Lunar, based on moon phases.
Why Is the Persian Calendar Considered More Accurate?
The Persian calendar is often considered more accurate than the Gregorian calendar because it aligns more closely with the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. This precision is due to the careful observation of equinoxes and solstices, which form the basis of the calendar. The result is a system that accurately tracks seasonal changes, making it invaluable for agricultural and meteorological purposes.
The Significance of the Persian Calendar in Modern Times
In today’s fast-paced world, the Persian calendar still holds immense significance. It serves as a reminder of the rich cultural heritage of Iran and the surrounding regions. The calendar’s accuracy and alignment with nature make it a valuable tool for various fields, including agriculture, astronomy, and environmental studies.
Moreover, the Persian calendar fosters a sense of identity and continuity. In a world where globalization often leads to cultural homogenization, the Persian calendar stands as a testament to the diversity and depth of human civilization. It reminds us that there are many ways to perceive and measure time, each with its own unique beauty and wisdom.
How Can the Persian Calendar Benefit You?
Understanding the Persian calendar can enrich your life in many ways. Whether you’re interested in cultural exchange, historical knowledge, or practical applications, the Persian calendar has something to offer. For example, if you’re into gardening or farming, the calendar’s alignment with seasons can help you plan your activities more effectively.
Conclusion: Embrace the Persian Calendar
In conclusion, the Persian calendar is more than just a system of counting days; it’s a celebration of culture, tradition, and nature. By understanding when the year 1404 begins and delving into the intricacies of the calendar, you gain a deeper appreciation for the world around you. So, whether you’re marking the date of Nowruz or simply learning about a different way of perceiving time, embrace the beauty of the Persian calendar.
Now it’s your turn. Share your thoughts in the comments below. Have you ever celebrated Nowruz? What fascinates you most about the Persian calendar? And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family. Let’s spread the knowledge and celebrate the diversity of our world together!
Federal Authorities Apprehend Longtime LA Gang Leader Suspected Of Murder And Human Trafficking
Freeze Warning For North Alabama Tonight; A Warmer Weekend Ahead
Survivor 50 Vote: The Ultimate Battle For Survival And Strategy

ساعت، تاریخ و لحظه تحویل سال ۱۴۰۳
تقویم کامل 1402 + ساعت سال تحویل
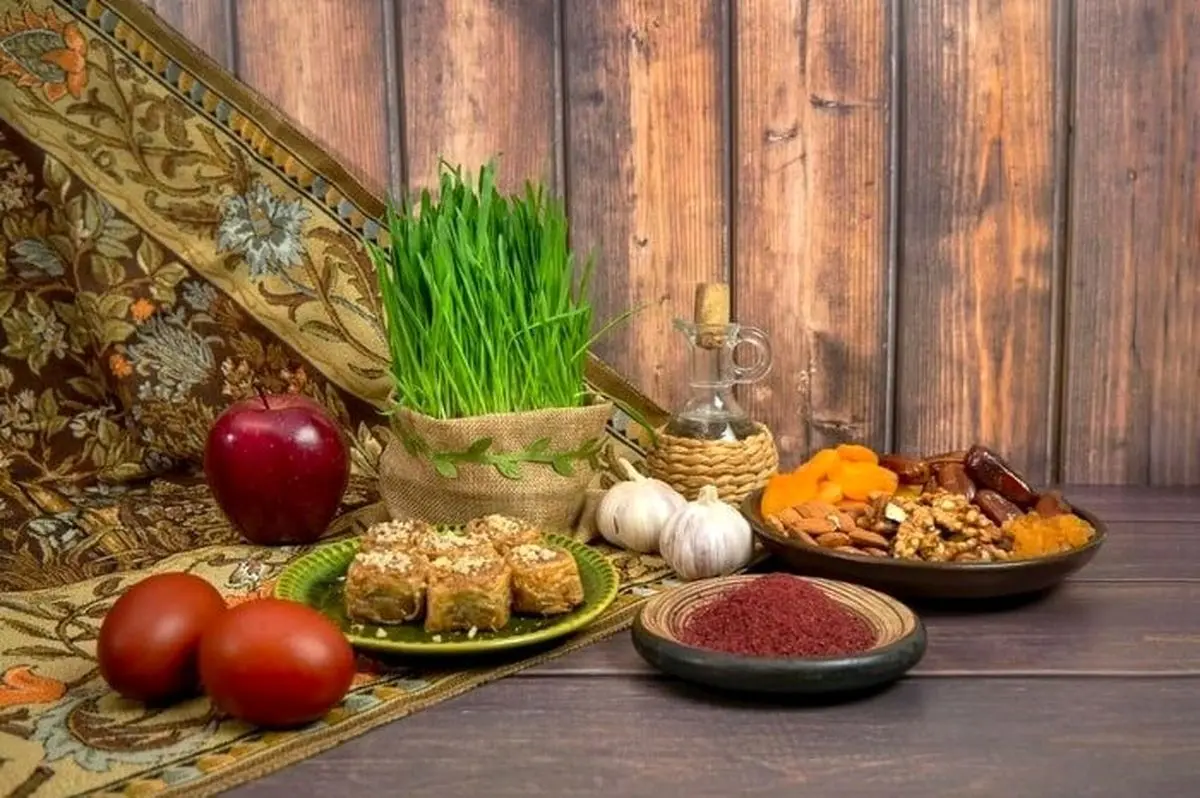

نکته خیلی مهم دربار ه لحظه تحویل سال ۱۴۰۴ که باید بدانید!